On September 27, 2024, LifeWatch ERIC will participate in the European Researchers’ Night, contributing to its programme and engaging with participants, thanks to its research stand.
On this occasion, LifeWatch ERIC will present in particular the project Marine SABRES (www.marinesabres.eu), organising the initiative “Marine SABRES in fairs: biodiversity conservation and restoration, sustainable blue economy and the benefits of ecotourism”.
Marine SABRES – Marine Systems Approaches for Biodiversity Resilience and Ecosystem Sustainability, is a research project funded by the European Union that aims to conserve and protect biodiversity by integrating healthy, sustainably-used ecosystems and a resilient blue economy. To make Ecosystem-based Management more achievable and implementable, Marine SABRES is comprehensively studying and analysing marine social-ecological systems to design a new, simpler framework for managing the many activities and pressures on the marine environment.
During the event, LifeWatch ERIC will present results and activities carried out in the framework of the project, with a special focus on this simple socio-ecological system framework designed and developed with the active support and participation of local stakeholders in three European marine regions, where researchers are developing and testing ways to balance varying combinations of conservation priorities and economic activities. The booth will promote best practices and examples, fostered by the project’s approach, of sustainable use of marine resources and tourism, raising awareness on the importance of governance solutions to address the impacts of future economic and climate scenarios.
Some videos realised by the LifeWatch Italy Multimedia Production Centre relating to project activities will be shown, and the research aims and results will be described with the help of posters and brochures. The videos will be also available to be broadcasted in a multimedia room.
For more information, please visit the official European Researchers’ Night ERN Apulia Med 2024
About the European Researchers’ Night
The European Researchers’ Night is a Europe-wide public event, which displays the diversity of science and its impact on citizens’ daily lives in fun, inspiring ways. The European Researchers’ Night aims to bring research and researchers closer to the public, promote excellent research projects across Europe and beyond, increase the interest of young people in science and research careers, showcase the impact of researchers’ work on people’s daily lives.
Children, young people, families and the general public at large will have the chance to meet researchers and discover research, science and innovation through a wide range of science shows, hands-on experiments, games, quizzes, competitions, exhibitions, digital activities, research stands, interactive workshops, debates and round tables, scientific-informative seminars, stories of researchers and discoveries, etc.
More information about the project
Biodiverse marine ecosystems provide flows of ecosystem services that lead to goods and benefits for society, support human well-being, and enable economic sustainability and resilience. Yet the intensification of human activities, both on land and at sea, is accelerating marine biodiversity loss globally and within Europe. The exploitation of natural resources, tourism, coastal development, trade and transport, aquaculture, fisheries, agriculture and waste management — all place pressures on marine and coastal ecosystems, undermining biodiversity and the many benefits that it provides. To mitigate these pressures, effective management of marine and coastal environments is essential, not only to achieve international biodiversity goals (such as the EU Biodiversity Strategy), but also in combating the threats of climate change (e.g. ocean warming, sea level rise, acidification, increased storminess) and environmental degradation (e.g. pollution and eutrophication).
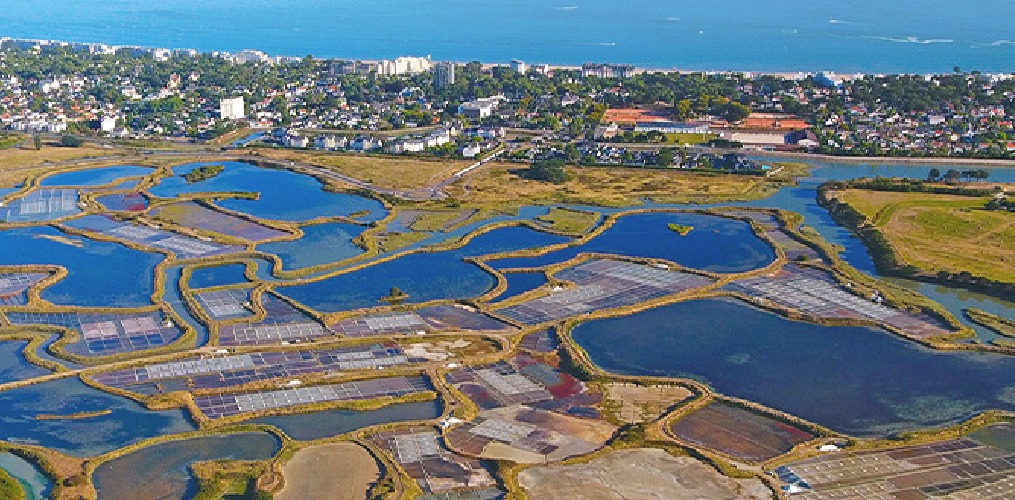
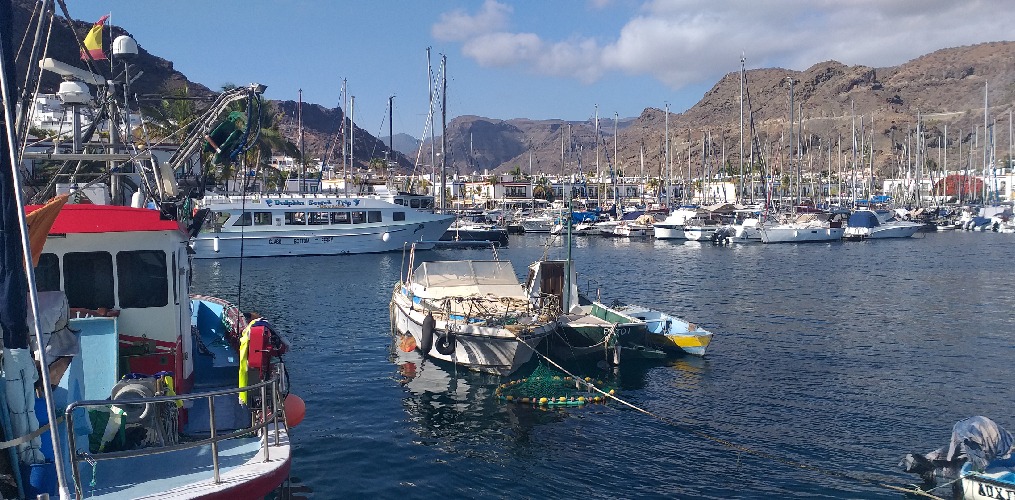
Marine SABRES is an EU-funded research project that aims to restore marine biodiversity and support a sustainable blue economy by increasing the uptake of ecosystem-based management in Europe. To make ecosystem-based management more achievable and implementable, we need to comprehensively study and analyse marine social-ecological systems. Marine SABRES is therefore co-developing and testing a simple socio-ecological system in collaboration with local people in three European marine regions: the Arctic Northeast Atlantic, the Tuscan Archipelago, and Macaronesia.
For more information, please visit Marine SABRES official website: www.marinesabres.eu
Watch our documentary trailers on LifeWatching WebTV platform: www.lifewatching.tv/tv-show/marine-sabres/