This story was originally published on LifeWatch Belgium.
A new LifeWatch Belgium paper compares two different marine soundscapes: the Gulf of Tribugá in Colombia and the the Belgian Part of the North Sea (BPNS). This study is of great importance as a general marine soundscape baseline in order to map possible future disturbances of port construction or to evaluate whether policy measures taken are effective. The comparison shows that biophony dominates the Gulf ot Tribugá while anthropophony is dominant in the BPNS.
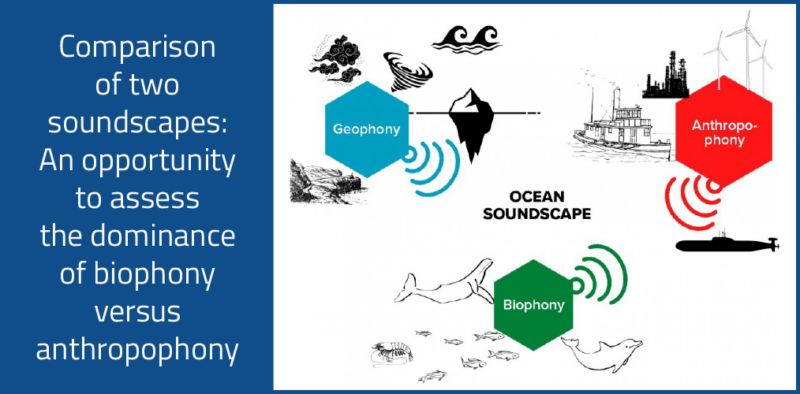
The “soundscape” of an ecosystem is defined as the characterisation of all the acoustic sources present in a certain place. A soundscape includes three fundamental sound source types: (1) anthropophony, or sounds associated with human activity; (2) biophony, or sounds produced by animals; and (3) geophony, or sounds generated by physical events such as waves, earthquakes, or rain. Studying soundscapes can provide information for a specific habitat, which could then be linked to ecosystem health status and other bioindicators. This information can be used to monitor the habitat over time, allowing for rapid detection of habitat degradation, such as in response to human-driven events. To do so, underwater recorders (hydrophones) are placed in different locations and are set to record broadband acoustic signals.
The paper describes two regions with vastly different marine soundscapes, characterised by extremely different shipping densities. The first study region, the Gulf of Tribugá, Colombia, is less affected by human activities. It serves as a general marine soundscape baseline for comparison with possible future disturbances from port construction and operation. By contrast, the second study region, the Belgian Part of the North Sea (BPNS) is located in a more disturbed area of very exploited shallow waters. Its baseline is being used to monitor the effects of noise reduction policies. The comparison shows that biophony dominates the Gulf ot Tribugá while anthropophony dominates the BPNS.
Read the whole paper via this link.
Image credit: Maria Paula Rey Baquero (Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Colombia)